Johari Window to Increase Your Self-Awareness
The Johari Window helps you gain self-awareness by revealing what is known and unknown to both yourself and others. It enhances communication and personal growth.

Johari Window is one of the most effective tools for developing self-awareness and improving communication skills. Johari Window is a psychological model that helps you to understand more about yourself (self-awareness) and in turn helps in self-improvement and improving yourself more effectively. It also encourages communicating and opening up with others resulting in enhanced communication skills. Seeing through the Johari Window helps you improving the quality of interpersonal communication. Johari Window model is based upon two things. First, to acquire the trust of others by revealing your information to them. Second, by learning about yourself through feedback by others.

Johari Window
Famous American psychologists Joseph Luft and Harry Ingham developed the Johari Window model in 1955. The name “Johari” comes from the combination of the first names of the two psychologists Joseph and Harry. Johari Window Model is also referred to as a “disclosure – feedback model of self awareness”. This model was originally developed for researching team’s group relations. Later on, it was found that the model can actually benefit every individual in their work and relationships. It has received great acceptability as a model for soliciting and giving feedback. Johari Window is a simple yet powerful tool for self-awareness.

The Johari Window model consists of four-quadrants, or four-pane, or window, or window pane.
Johari Window Quadrant 1 – Arena (Open Area/Open Self)
It is the Open Area of a person’s life where things are known both to the person and to others. This is the area in which you should generally operate to be effective in interpersonal relationship. One key to success in mastering interpersonal skills is to know about self and the people to whom you interact, which can be done by operating in this area. The larger this area, the greater the individual’s contact is with the actual world. He/she is more available with his abilities and needs to self as well as others.
This part includes all the information that the individual willingly and openly shares with other people through the diverse communication media: dress code, behavior, body language, knowledge, skills, attitudes, “public” history, tone of voice, gestures and words etc.
Johari Window Quadrant 2 – Blind spot (Blind Area/Blind Self)
It contains things unknown to the individuals about themselves, but known to those around them. This is the Blind Area of a person’s life. Feedback from others is the way to decrease this Blind Area and enlarge the Open Area. In the Blind Area, we are more likely to unknowingly hurt other people and do things they do not like. The blind area traits are more or less governed by unconscious mind. The person behave unknowingly. Habits also make a person to act in a unknowingly way which cant hurt others.
Johari Window Quadrant 3 – Facade (Hidden Area/Hidden Self)
It is the hidden part of a person’s life where things are known to the person but not to the others. That’s why you may also call this area as Hidden Area. This part hides all that kind of information that we don’t feel comfortable to share with others. This area generally contains an individual’s emotions, feelings, opinions, prejudices and past history or experiences.
Minimizing these hidden things improve interpersonal relationships in your work and in your personal lives.
Johari Window Quadrant 4 – Unknown (Dark Area/Unknown Self)
This is the Unknown Area of a person’s life where things are not known to that person or to others. You may also call this area the Undiscovered Self or the Dark Area. By self-discovery and other’s observation, you can reduce the Unknown Area. Always encourage yourself to encounter new and different situations.
Operating in this area often leads to misunderstanding which creates interpersonal conflict.
Advantages/Disadvantages of Johari Window
Here are advantages and disadvantages of Johari Window :

Advantages/Benefits of Johari Window
Well now you have fair bit of idea what Johari Window model is all about? This model can be pretty useful for understanding your relationship with self and others. It is of utmost importance to have a good relationship with self and having a good relationship with self helps you to improve your relationships with others. A good self-relationship enhances your capability to value yourself as a person. Johari Window helps people first to understand them better, and then improvising their vital relations in life. Here are the benefits of using Johari Window
- self-awareness
- better communication skills
- improved interpersonal skills
- high self-esteem
- more self-confidence
- improved trust in relationships
- know more about your strength and weaknesses
Disadvantages/Drawbacks of Johari Window
Like any other model, there are some drawbacks and disadvantages of Johari Windows as well. These are:
- In my opinion, few things are perhaps, which better should not be communicated with others.
- Confidentiality can be compromised. People may pass on the information they received further than you desire or use it in a negative way.
How to use Johari Window Model for Self-Awareness
Now coming to the point how to use Johari Window? Understanding Johari Windows actually helps in shifting your quadrants. In order to get the most out of the Johari Window self analysis, you need to be work with some other people who know them well. For instance, family members, co-workers, friends, etc.
The first step is – Describe your Johari Window. Which area or areas are largest for you? And which are Smallest? To do this, first of all put your abilities, competencies, traits, behaviors, motives, strengths and weaknesses in the three quadrants Open Area/Open Self, Blind Area/Blind Self and Hidden Area/Hidden Self. Secondly, ask your close and trustworthy friends or relatives; who know about you well do the same for you i.e. putting your abilities, competencies, traits, behaviors, motives, strengths, and weaknesses in the three quadrants Open Area, Blind Area and Hidden Area.
The results of the Johari Window exercise may differ depending on whether you do the exercise with friends, coworkers, or family. You can do the exercise with people in all three groups and then analyze the results.
Now once your Johari Window is ready as mentioned above, the ultimate goal is to enlarge your OPEN AREA in both sides vertically as well as horizontally. The ideal Johari Window has a large Open Area. This is because, the more you know about yourself and others, the more productive, cooperative and trusting you’ll be.
Self disclosure: Enlarging Vertically
You can move information from the Hidden Self to the Open Self through self disclosure. The process of enlarging the Open Area vertically is self – disclosure. A give and take process between you and the people you interact with. When you share information through self – disclosure, the boundary with the Hidden Area moves downwards. And, as other people reciprocate, trust tends to build between you and them. This leads to stronger communication and bonding.
Well, I don’t advise you to be rash in your self disclosure. Disclosing harmless items helps to build trust. However, disclosing information which could damage other people’s respect for you can put you in a position of weakness. You should also demonstrate empathy towards others and a concern for others.
Feedback: Enlarging Horizontally
You can move information from the Blind Self to the Open Self through feedback. The process of enlarging the Open Area horizontally is feedback; it is also a give and take process between you and the people you interact with. Here you will learn things about you that others can see, but you can’t. For example, you might not realize that you are impulsive and have anger issues until someone points it out to you. Active and emphatic listening skills are useful in this process. By asking/soliciting feedback, and by being open to feedback by others, you become more aware of how others perceive you. By doing this you shrink your Blind Area.
A small Blind Area indicates that you’re aware of how your behavior affects other people, whereas a large Blind Area suggests that you may be naive or even in denial about it
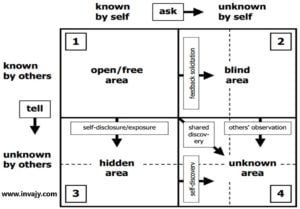
Self / Shared Discovery
This is enlarging the Open Area diagonally. Since Unknown Area is neither known by you nor others here self-discovery, combined or shared discovery and others observations can help enlarging Open Area/Open Self (Quadrant 1) and shrink Unknown Area/Unknown Self (Quadrant 4). A large Unknown Area may just be a sign of youth or inexperience, but it can also mean that you need to work hard on discovering and releasing new information about yourself. And that becomes possible through self/shared discovery.
Wrapping Up!
When you know about yourself and about others; it becomes easier to transact with each other. By encouraging healthy self-disclosure and sensitive feedback, your enlarged Open Area or Free Area or Open Self or Arena boosts your self-awareness.
That’s all from my side about Johari Window Model, it’s benefits and how to use it. Thank you for reading this. Please add your valuable comments, they are much appreciated.
If you have liked this article please share it with your friends and relatives on your favorite social media websites/apps.






very useful and efficient tool
excellent work
educational
usefull
thanking you with best wishes